When it comes to the internal combustion engine, few components are as fundamental as the engine block. Often referred to as the “heart of the engine,” the engine block houses the essential components that generate power and ensure the engine functions reliably. Despite being a solid-looking chunk of metal, the engine block is a complex piece of engineering that plays a central role in the performance, durability, and efficiency of your car’s engine.
In this article, we’ll explore the structure, materials, function, and common issues of the engine block — and how to know when it might need repair or replacement.
What Is the Engine Block?
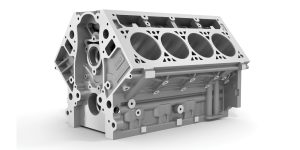
The engine block is the main structure of an internal combustion engine. It contains the cylinders where pistons move up and down, converting fuel into mechanical power. The block also serves as the mounting point for other key components like the crankshaft, oil pump, and cylinder head.
Key Functions of the Engine Block
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Cylinder Housing | Provides the space for pistons to move and create combustion. |
| Structural Support | Acts as the base for attaching the crankshaft, camshaft, and cylinder head. |
| Coolant and Oil Flow | Contains internal passages for circulating coolant and lubricating oil. |
| Heat Dissipation | Helps regulate engine temperature by distributing and releasing heat. |
Main Components Contained in the Engine Block
-
Cylinders: The chambers where fuel is burned and pistons move.
-
Crankshaft Housing: Where the crankshaft converts piston movement into rotational motion.
-
Oil Passages: Channels that carry engine oil to lubricate moving parts.
-
Coolant Passages: Allow coolant to flow through and remove excess heat.
-
Main Bearings: Support the crankshaft and allow smooth rotation.
-
Deck Surface: The flat top where the cylinder head is bolted.
Materials Used in Engine Block Manufacturing
| Material | Characteristics | Common Use |
|---|---|---|
| Cast Iron | Durable, excellent wear resistance | Older cars, heavy-duty engines |
| Aluminum Alloy | Lightweight, good heat dissipation | Most modern cars and high-performance engines |
| Compacted Graphite Iron (CGI) | Stronger than cast iron, lighter | Diesel and performance applications |
Types of Engine Blocks
| Type | Description | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Inline Block | Cylinders arranged in a straight line | Simpler design, compact |
| V-Type Block | Cylinders arranged in a V shape over a common crankshaft | More cylinders in smaller space |
| Opposed (Boxer) Block | Horizontally opposed cylinders | Low center of gravity, smoother operation |
How the Engine Block Affects Performance
The condition and design of the engine block influence:
-
Power Output: Efficient cylinder design improves combustion.
-
Fuel Efficiency: Proper sealing and lubrication reduce energy loss.
-
Engine Lifespan: Strong block materials resist wear and stress.
-
Thermal Management: Internal cooling passages help avoid overheating.
Common Engine Block Problems

Though built to last, engine blocks are not immune to damage. Here are common issues:
1. Cracks in the Block
-
Cause: Overheating, freezing coolant, or impact damage.
-
Symptoms: Coolant leaks, white exhaust smoke, engine overheating.
2. Warped Cylinder Walls
-
Cause: Severe overheating.
-
Symptoms: Loss of compression, poor performance, misfires.
3. Worn Bearings or Journals
-
Cause: Lack of lubrication or dirty oil.
-
Symptoms: Knocking sounds, low oil pressure, bearing failure.
4. Blown Head Gasket (affecting block deck)
-
Cause: Overheating, improper installation.
-
Symptoms: Milky oil, overheating, coolant loss.
How to Prevent Engine Block Damage
Regular maintenance and smart driving habits go a long way in preserving the integrity of your engine block.
-
Check Coolant Levels Regularly to prevent overheating.
-
Change Oil on Schedule to ensure proper lubrication.
-
Watch the Temperature Gauge to catch overheating early.
-
Avoid Hard Driving on Cold Engines, which stresses internal parts.
-
Use the Correct Coolant Mixture to avoid freezing or corrosion.
Engine Block Repair or Replacement: What to Consider
Repair May Be Possible If:
-
Cracks are minor and accessible for welding or epoxy.
-
Warping can be corrected by machining.
-
Cylinder walls can be re-bored or sleeved.
Replacement Is Often Necessary When:
-
Damage is severe or widespread.
-
Repair costs approach or exceed replacement value.
-
You’re rebuilding an engine for performance or longevity.
If you’re in need of a replacement, you can Buy Engine Block online and choose from a range of high-quality parts suited to your vehicle.
Summary: Why the Engine Block Matters
| Key Role | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Structural Foundation | Supports and aligns all engine components |
| Combustion Chamber Housing | Enables fuel combustion and power generation |
| Lubrication and Cooling Pathways | Keeps engine running smoothly and efficiently |
| Performance and Longevity | Directly influences power, efficiency, and life |
Final Thoughts
The engine block is not just a chunk of metal — it’s a precisely engineered component that forms the backbone of your car’s powerplant. Whether you’re maintaining your daily driver or rebuilding a high-performance engine, understanding the structure and function of the engine block helps you make smarter decisions.
If you need a new block or related parts, explore your options and Buy Engine Block online for quality, convenience, and compatibility.